Introduction
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN) is a benign epidermal proliferation, often described as a variant of seborrheic keratosis, characterized by multiple small, pigmented papules on the face and neck. Though asymptomatic, DPN frequently drives cosmetic concern and patient self-consciousness, making safe, precise clearance a key goal for dermatologists.
Clinical highlight
Radiofrequency electrocautery offers rapid, controlled lesion clearance with low downtime and minimal pigmentary risk when energy delivery is conservative and post-care is strict.
Case presentation
A 32-year-old female presented with gradually increasing, asymptomatic dark papules over the malar and periorbital areas for approximately 4 to 5 years. Lesions caused cosmetic dissatisfaction without pain, bleeding, itching, or sudden morphologic change. Examination revealed multiple discrete, smooth, hyperpigmented papules (1 to 4 mm), sessile to minimally pedunculated, with a classic "stuck-on" appearance consistent with DPN.
Diagnostic approach
Diagnosis was clinical, based on typical morphology, color, and facial distribution, along with absence of inflammation or rapid growth. Differential diagnoses considered and excluded:
- Seborrheic keratosis
- Melanocytic nevi
- Verruca plana
- Syringomas
Given the classic presentation, histopathology was not required before treatment.
Pathophysiology
DPN represents a benign epidermal proliferation with increased melanin content. Key contributors include genetic predisposition, increased melanocyte activity, and age-related epidermal changes. It is most common in Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI and often demonstrates a familial pattern, with lesion number and size increasing over time.
Treatment approach
After counseling on risks (post-inflammatory pigmentation, recurrence), lesions were treated using radiofrequency electrocautery.
Procedure details
- Topical anesthesia applied before the procedure
- Individual lesions coagulated with a fine RF needle in low-power coagulation mode
- Thermal spread minimized to preserve surrounding skin; immediate hemostasis achieved
The procedure was well tolerated with minimal discomfort and high precision.
Post-operative care
- Topical fusidic acid twice daily for 5 days to prevent infection
- Short course analgesic/anti-inflammatory (e.g., Enzoflam) for 2 to 3 days as needed
- Strict photoprotection, avoidance of picking or friction, and gentle cleansing
Immediate post-procedure appearance showed superficial crusting without excessive erythema.
Additional treatment modalities
Depending on lesion size, count, skin type, and patient preference, other options include:
- Electrocautery
- Cryotherapy (cautious use due to pigmentary risk)
- Laser therapies: Nd:YAG or CO2 in selected cases
- Shave excision for larger pedunculated lesions
Radiofrequency ablation remains preferred for DPN due to accuracy, speed, and low scarring risk when executed conservatively.
Clinical implications
Even benign lesions can strongly impact self-image. Controlled energy delivery and disciplined aftercare reduce dyspigmentation risk in darker skin types, while setting expectations about possible recurrence maintains trust.
Clinical results
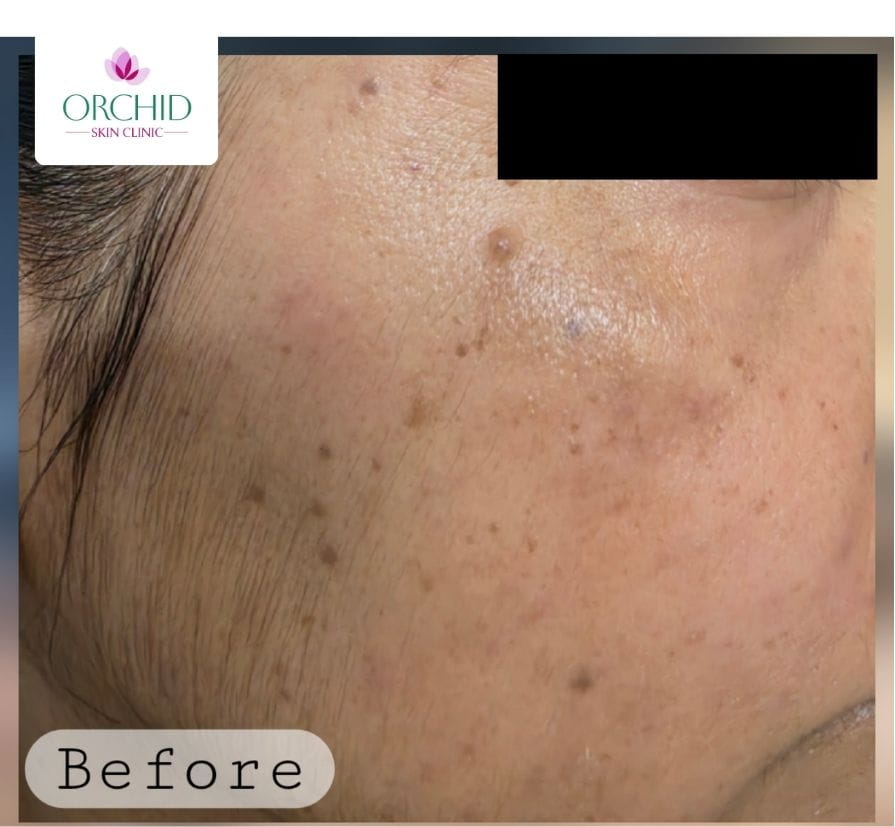
Before Treatment
Multiple hyperpigmented papules over the malar and periorbital region causing cosmetic concern.
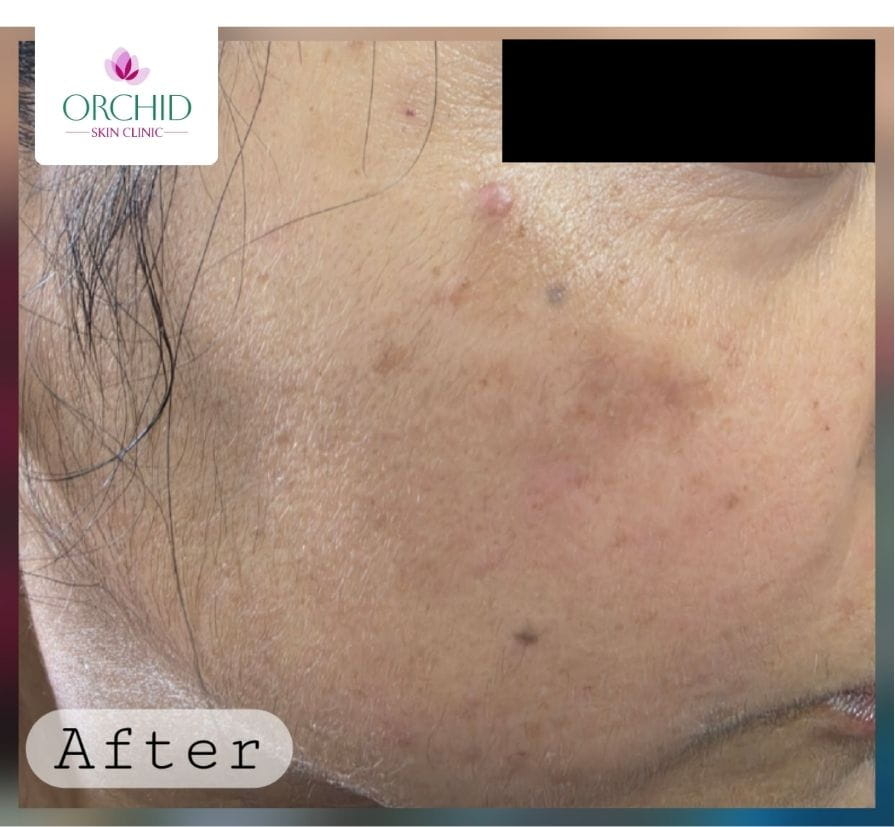
4 Weeks Post RF Electrocautery
Clearance of papules with smooth skin tone and no visible dyspigmentation after conservative energy delivery.
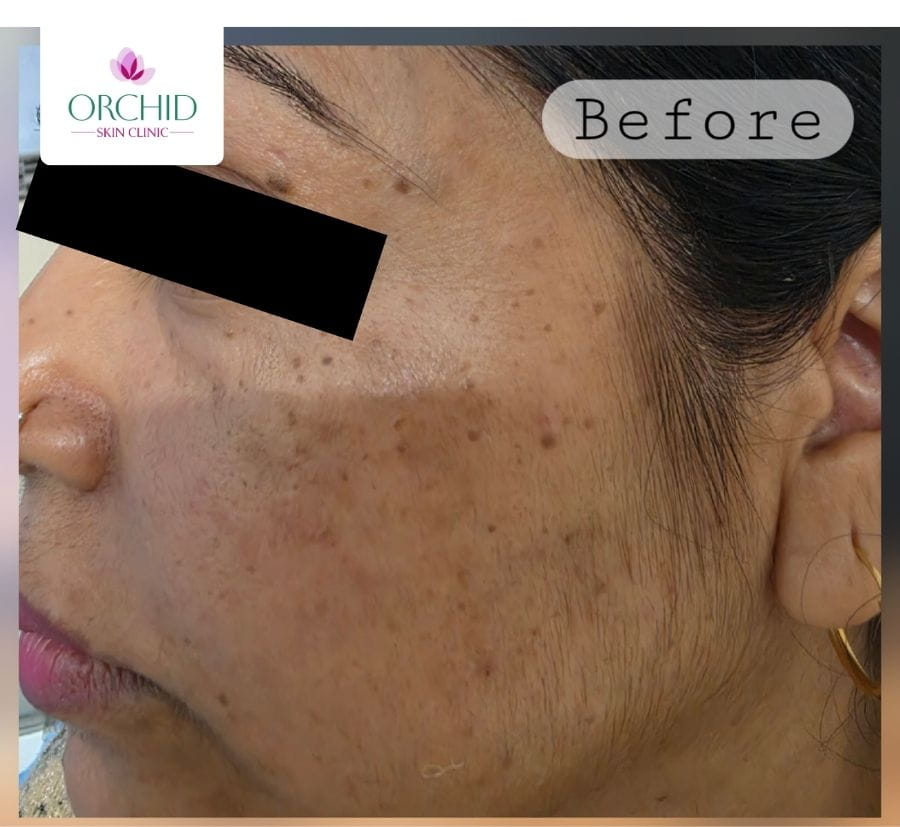
Before Treatment (Case 2)
Clustered papules along the lateral cheek awaiting conservative RF clearance.
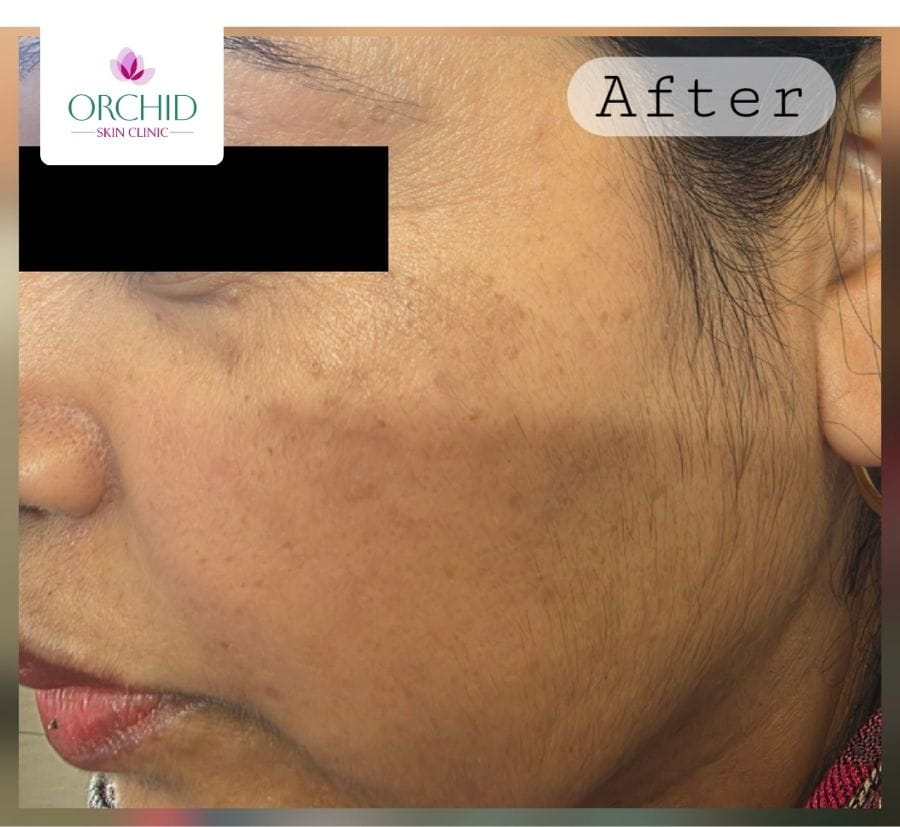
3 Weeks Post RF (Case 2)
Even skin tone with resolved papules and no visible post-inflammatory dyspigmentation.
Replace the placeholders above with the final before/after photos once available.
Conclusion
A 32-year-old female with dermatosis papulosa nigra achieved uniform clearance using radiofrequency electrocautery with excellent cosmetic improvement and high satisfaction. RF ablation is a safe, office-based approach when paired with conservative settings and diligent post-procedure care.